-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 16
TestClassifier Tutorial
TestClassifier tests a classifier created by TrainClassifier to see how it performs on a test set. Remember, a classifier classifies an entire document, so the result of this experiment simply outputs statistics about how many documents are labeled correctly. For this example, we will use the classifier obtained by running the example in the TrainClassifier Tutorial. For quick reference here is the command line experiment to obtain the classifier that will be used in this example (samples are built into code, so no setup is required to make them work):
$ java –Xmx500M edu.cmu.minorthird.ui.TrainClassifier –labels sample3.train –spanType fun –saveAs sample3.annsample3.ann is the classifier that is saved and used for this experiment; it classifies which documents are "fun". To see how to label and load your own data for this task, look at the Labeling and Loading Data Tutorial.
To run this type of task start with:
$ java –Xmx500M edu.cmu.minorthird.ui.TestClassifierLike all UI tasks, all the parameters for TestClassifier may be specified either using the GUI or the command line. To use the GUI, simply type –gui on the command line. It is also possible to mix and match where the parameters are specified. For example, one can specify two parameters on the command line and use the GUI to select the rest. For this reason, the step-by-step process for this experiment will first explain how to select a parameter value in the GUI and then how to set the same parameter on the command line.
To view a list of parameters and their functions run:
$ java –Xmx500M edu.cmu.minorthird.ui.TestClassifier –helpor
$ java –Xmx500M edu.cmu.minorthird.ui.TestClassifier –guiClick on the Parameters button next to Help or and click on the ? button next to each field in the Property Editor to see what it is used for. If you are using the GUI, click the Edit button next to TestClassifier. A Property Editor window will appear:

There are four bunches of parameters to specify for this experiment. A collection of documents (labelsFilename), an Annotator (loadFrom), and spanType or spanProp are required. All other fields are optional. For more information about any of these fields, click on the ? (help button) next to the field.
-
baseParameterscontains the options for loading the collection of documents. - GUI: enter
sample3.testin thelabelsFilenametext field;sample3.testcontains labeled documents, but it is useful for comparing true labels to predicted labels. - Command Line: use the
–labelsoption followed by the repository key or the directory of files to load. In this case specify–labels sample3.test. -
saveParameterscontains one parameter for specifying a file to save the result to. Saving is optional, but useful for using result in other experiments or for reference. It is useful to save in the formatLABELS_FILENAME.labelswhereLABELS_FILENAMEis the directory entered in thelabelsFilenametext field. This way MinorThird can automatically load the labels produced by this experiment in another MinorThird task. - GUI: type
sample3.labelsin thesaveAstext field. - Command Line:
-saveAs sample3.labels -
signalParameters: eitherspanTypeorspanPropmust be specified as the type to learn. For this experiment we will use span typefun. - GUI: Click the
Editbutton next tosignalParameters. Selectfunfrom the pull down menu next tospanType. - Command Line:
–spanType fun -
additionalParameterscontains one parameter for specifying the annotator to load. - GUI: enter
sample3.ann(or the file name you chose for your annotator) in theloadFromtext field. - Command Line:
-loadFrom sample3.ann(or the file name you chose for your annotator) - Feel free to try changing any of the other parameters including the ones in
advanced options. - GUI: Click on the help buttons to get a feeling for what each parameter does and how changing it may affect your results. Once all the parameters are set, click the
OKbutton onProperty Editor. - Command Line: Add other parameters to the command line (use
–helpoption to see other parameter options). If there is an option that can be set in the GUI, but there is no specific parameter for setting it in the help parameter definition, the–otheroption may be used. To see how to use this option, look at the Command Line Other Option Tutorial. - If you are using the GUI, once finished editing parameters, save parameter modification by clicking the
OKbutton onProperty Editor.
- GUI: press the
Show Labelsbutton if you would like to view the input data for the classification task. - Command Line: add
–showLabelsto the command line.
- Opening the result window:
- GUI: Press
Start TaskunderExecution Controlsto run the experiment. The task will vary in the amount of time it takes depending on the size of the data set and what learner and splitter you choose. When the task is finished, the error rates will appear in the output text area along with the total time it took to run the experiment. - Command Line: specify
–showResult(this is for seeing the graphical result, if this option is not set, only the basic statistics of the task will be seen).
-
Once the experiment is completed, click the
View Resultsbutton in theExecution Controlssection to see detailed results in the GUI. The window will automatically appear if the–showResultoption was specified on the command line. TheTest Partitiontab shows the testing examples in the top left, the classifier in the top right, the selected test example's features, source, and subpopulation in the bottom left, and the explanation for the classification of the selected test example in the bottom right (expand the tree to see the details of the explanation).
-
Click on the
Overall Evaluationtab at the top and theSummarytab below that to view your results. The summary tab shows you the results that were printed in the output window when you ran the experiment (it shows you the numbers like error rate and F1). ThePrecision/Recalltab shows you the graph of recall vs. precision for this experiment. TheConfusion Matrixtab shows you how many things the classifier predicted as positive that are positive and how many that it predicted as positive that are negative and vice versa.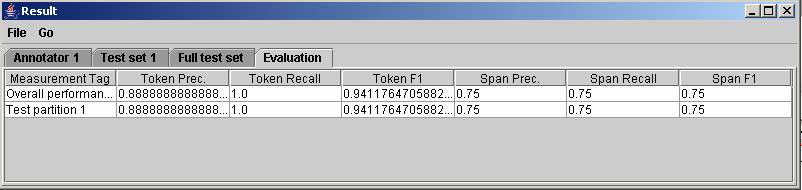
-
Press the
Clear Windowbutton to clear all output from the output and error messages window.