Connect NodeMCU (ESP8266) to AWS IoT: Medium
The AwsIotWiFiClient library is designed to facilitate the connection of ESP8266 devices to AWS IoT Core. This library provides an abstraction layer that simplifies the process of establishing secure SSL/TLS communication and MQTT messaging between the ESP8266 microcontroller and AWS IoT services.
- Secure Communication: uses WiFiClientSecure to manage certificates and private keys, ensuring secure communication with AWS IoT Core. Unlike other libraries that require creating policies and making direct calls, AwsIotWiFiClient establishes secure communication using device certificates, which is the native approach for AWS IoT.
- MQTT Messaging: incorporates the PubSubClient library to support MQTT messaging, allowing devices to publish and subscribe to topics on AWS IoT Core.
- Easy Configuration: provides a straightforward API for setting up certificates, endpoints, client IDs, and topic filters.
- Callback Mechanism: supports callback function to handle incoming MQTT messages, enabling real-time data processing and event handling.
- Debugging: offers debug output to assist in troubleshooting and verifying the connection and communication processes.
The AwsIotWiFiClient library is ideal for projects that involve ESP8266 devices needing to communicate with AWS IoT Core. Typical applications include sensor data collection, remote monitoring, and control systems where reliable and secure data exchange is critical.
By abstracting the complexity of secure communication and MQTT messaging, the AwsIotWiFiClient library allows developers to focus on implementing the business logic of their IoT applications.
#include "AwsIotWiFiClient.h"
#include "ESP8266WiFi.h"
#include "pgmspace.h"
// Device certificate
// Copy and paste contents from *-certificate.pem.crt
static const char deviceCertificate[] PROGMEM = R"KEY(
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
)KEY";
// Key files / Private key file
// Copy and paste contents from *-private.pem.key
static const char privateKeyFile[] PROGMEM = R"KEY(
-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
-----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
)KEY";
// RSA 2048 bit key: Amazon Root CA 1
// Copy and paste contents from AmazonRootCA1.cer
static const char rootCaCertificate[] PROGMEM = R"EOF(
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
)EOF";
AwsIotWiFiClient awsIotWiFiClient;
BearSSL::X509List trustAnchorCertificate(rootCaCertificate);
BearSSL::X509List clientCertificate(deviceCertificate);
BearSSL::PrivateKey clientPrivateKey(privateKeyFile);
void receiveMessage(char *topic, byte *payload, unsigned int length)
{
Serial.print("Message received: ");
Serial.write(payload, length);
Serial.println();
}
void setup()
{
// Connect to Wi-Fi first!
// ...
// Set up AWS IoT Wi-Fi Client:
awsIotWiFiClient
// Enable debug output:
.setDebugOutput(true)
// Certificates to establish secure communication (defined above):
.setCertificates(&trustAnchorCertificate, &clientCertificate, &clientPrivateKey)
// Device Data Endpoint from IoT Core -> Settings:
.setEndpoint("endpoint.iot.us-east-1.amazonaws.com")
// Callback function that will be triggered when incoming messages are received (defined above):
.setReceiveMessageCallback(receiveMessage)
// MQTT client ID aka thing name:
.setClientId("client")
// MQTT topic filter to subscribe to incoming messages:
.setSubscribeTopicFilter("topic")
// Connect to the AWS IoT service:
.connect();
}
void loop()
{
// ...
// Publish message "Hello, world!" to the "topic" topic:
awsIotWiFiClient.publishMessage("topic", "Hello, world!");
awsIotWiFiClient.loop();
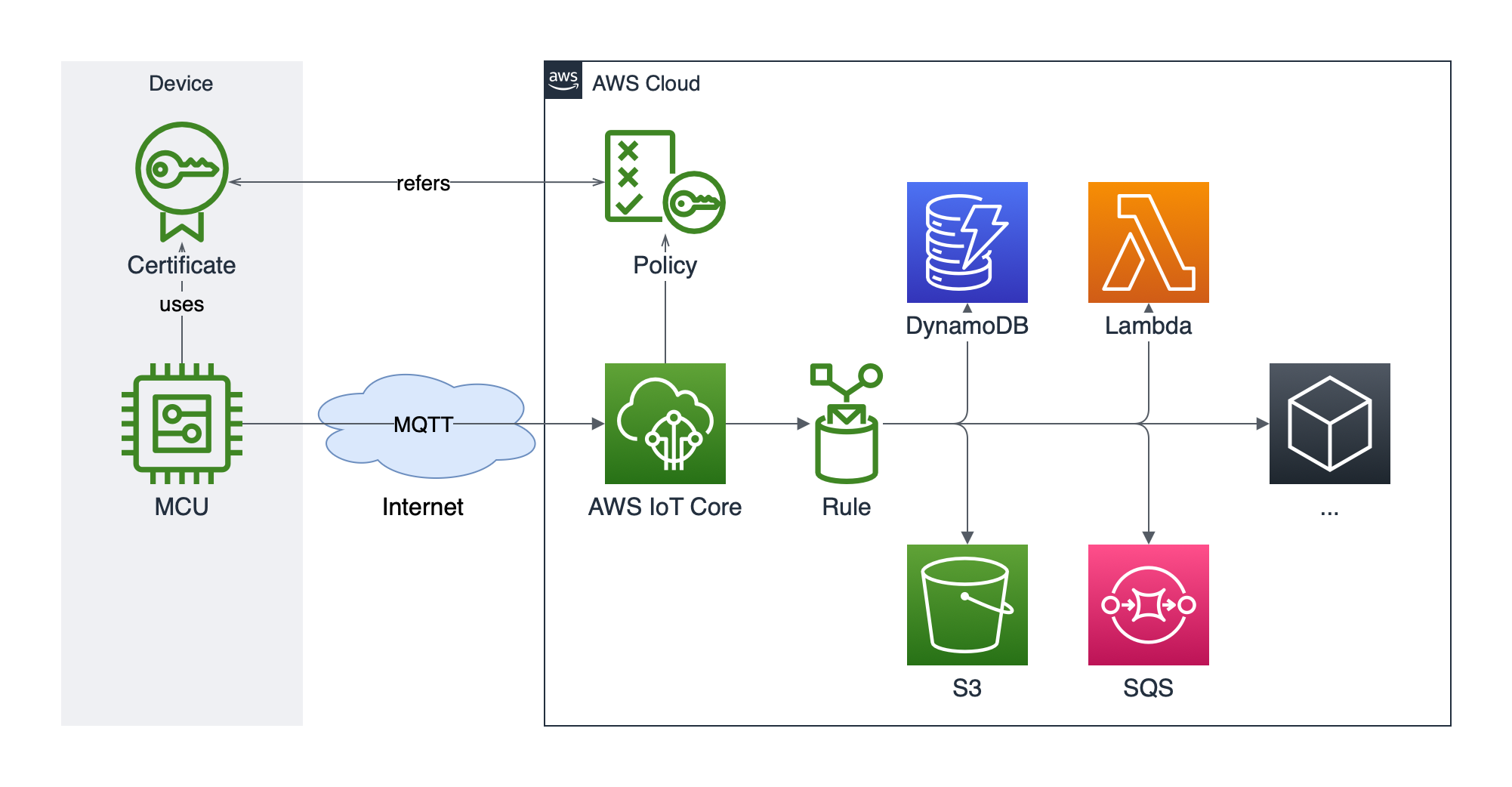
}There are several additional AWS components shown on the right, beyond the AWS IoT Core, but they are just an example of how you can further extend the solution, while we are going to focus on the central and left parts:
- AWS IoT Core configuration;
- Microcontroller (MCU) connection over MQTT to AWS IoT Core;
- Device certificate and policy that will grant necessary permissions to establish a connection, publish, and receive messages from AWS IoT Core.
MQTT has gained popularity within the hobbyist community for DIY IoT projects due to its simplicity and efficiency. AWS IoT leverages MQTT as a standard to enable seamless, real-time data exchange between IoT devices and the cloud, making it ideal for connecting constrained devices like the NodeMCU.
Device certificate ensures that the communication between your microcontroller and AWS is encrypted and secure, but also authenticates your device with AWS IoT, confirming its identity — this guarantees that only trusted devices can connect to your AWS infrastructure, maintaining the integrity of your system.
AWS IoT Wi-Fi Client class is the core component of the library, encapsulating all the functionalities needed to connect an ESP8266 microcontroller to AWS IoT Core. It manages the setup of secure SSL/TLS communication using WiFiClientSecure and facilitates MQTT messaging via PubSubClient.
The class provides methods to configure device-specific credentials, establish connections, and subscribe to and publish MQTT messages. Additionally, it includes a callback mechanism to process incoming messages.
Kind: class
Set certificates to establish secure communication.
Kind: instance method of AwsIotWiFiClient
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| &trustAnchorCertificate | X509List* |
Pointer to the trust anchor certificate |
| &clientCertificate | X509List* |
Pointer to the client certificate |
| &clientPrivateKey | PrivateKey* |
Pointer to the client private key |
Set Device Data Endpoint from IoT Core -> Settings.
Kind: instance method of AwsIotWiFiClient
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| endpoint | char* |
Device Data Endpoint |
Set the callback function that will be triggered when incoming messages are received.
Kind: instance method of AwsIotWiFiClient
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| callback | std::function<void(char *, uint8_t *, unsigned int)> |
Function to call when an incoming message is received |
Example:
void callback(char *topic, byte *payload, unsigned int length)
{
Serial.print("Message received: ");
Serial.write(payload, length);
Serial.println();
}Set the MQTT client ID aka thing name.
Kind: instance method of AwsIotWiFiClient
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| clientId | char* |
MQTT client ID |
Set the MQTT topic filter to subscribe to incoming messages.
Kind: instance method of AwsIotWiFiClient
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| subscribeTopicFilter | char* |
MQTT topic filter |
Enable or disable debug output. Disabled by default.
Kind: instance method of AwsIotWiFiClient
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| debugOutput | boolean |
true to enable, false to disable debug output |
Connect to the AWS IoT service.
Kind: instance method of AwsIotWiFiClient
Keep the MQTT connection alive and process incoming messages. This should be called regularly in the main loop.
Kind: instance method of AwsIotWiFiClient
Publish a message to the specified MQTT topic.
Kind: instance method of AwsIotWiFiClient
Returns: boolean - true in case of success, or false otherwise
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| topicName | char* |
The MQTT topic to publish to |
| message | char* |
The message payload |